Passive Q-Switch Lasers
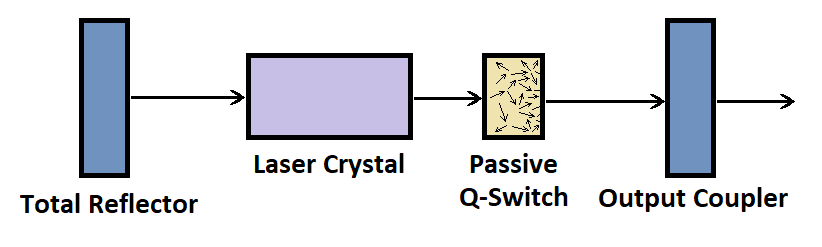 Passive q-switches use a saturable absorber, which can be a crystal (typically Cr:YAG), a passive semiconductor, or a special dye. Passive q-switches take advantage of a process known as saturable absorption. Saturable absorption derives from the fact that there is a limit to the amount of light that a material can physically absorb at a given wavelength before the energy level becomes saturated and the material becomes temporarily transparent. As a result, if a saturable absorbing material is placed inside of the laser cavity, it will absorb all of the spontaneously emitted photons until it reaches saturation where it will then allow the photons to pass through and initiate stimulated emission. In a saturable absorber, the time it takes for for excitation to resolve after after stimulation by an energy source is referred to as recovery time. Ideally, the recovery time is some period longer than that of the pulse duration. This condition helps avoid undesired energy loss. However, if recovery time is too long, premature lasing can occur when the laser’s gain recovers and the saturable absorber is still ‘open.’ A good rule of thumb is to have a recovery time that is longer than the pulse duration, but shorter than the upper-state lifetime of the gain medium to avoid unwanted lasing and pulse issues.
Passive q-switches use a saturable absorber, which can be a crystal (typically Cr:YAG), a passive semiconductor, or a special dye. Passive q-switches take advantage of a process known as saturable absorption. Saturable absorption derives from the fact that there is a limit to the amount of light that a material can physically absorb at a given wavelength before the energy level becomes saturated and the material becomes temporarily transparent. As a result, if a saturable absorbing material is placed inside of the laser cavity, it will absorb all of the spontaneously emitted photons until it reaches saturation where it will then allow the photons to pass through and initiate stimulated emission. In a saturable absorber, the time it takes for for excitation to resolve after after stimulation by an energy source is referred to as recovery time. Ideally, the recovery time is some period longer than that of the pulse duration. This condition helps avoid undesired energy loss. However, if recovery time is too long, premature lasing can occur when the laser’s gain recovers and the saturable absorber is still ‘open.’ A good rule of thumb is to have a recovery time that is longer than the pulse duration, but shorter than the upper-state lifetime of the gain medium to avoid unwanted lasing and pulse issues.
Our Products
RPMC offers a selection of passively Q-switched lasers, including Pulsed DPSS Lasers, Ultrafast Lasers, Microchip Lasers (Microlasers), and MIL-Spec. Lasers. Wavelength options include the UV, Blue, Green, NIR, and SWIR spectral regions, and pulse width options available from 40ns down to 7 ps.
Let Us Help
In conclusion, if you have any questions or would like some assistance please contact us here. Furthermore, you can call us at 636.272.7227 to talk to a knowledgeable Product Manager. Alternatively, use the filters on this page, or check out our ‘How to Select a Pulsed Laser‘ version of this page to assist in narrowing down the selection. Finally, head to our Knowledge Center with our Lasers 101 page and Blogs and Whitepapers pages for further, in-depth reading.
Suggested Reading
“The Advantages and Disadvantages of Passive vs Active Q-Switching”






 The OT series of Erbium Glass lasers are ultra-compact, high energy q-switched, solid-state lasers that are well suited for rugged, field applications such as active night vision and rangefinding. These air-cooled lasers are available in both lamp-pumped and diode-pumped configurations, with passive and active Q-switching options. With over 10,000 units in the field, the OT series is a proven technology operating in some of the more challenging laser environments.
The OT series of Erbium Glass lasers are ultra-compact, high energy q-switched, solid-state lasers that are well suited for rugged, field applications such as active night vision and rangefinding. These air-cooled lasers are available in both lamp-pumped and diode-pumped configurations, with passive and active Q-switching options. With over 10,000 units in the field, the OT series is a proven technology operating in some of the more challenging laser environments.